
Mercuric chloride - HgCl2
What is Mercuric chloride?
HgCl2 is a chemical compound formed by mercury and chlorine with a chemical name Mercuric chloride. It is also called Mercury(II) chloride, Mercury dichloride, or Dichloromercury. It is highly a toxic compound and is corrosive to mucous membranes.
It is widely used as a disinfectant, antiseptic, fungicide, wood preservative.
Mercury dichloride is odourless crystalline solid white in colour. It is a triatomic molecule where a mercury atom is bonded with two chlorines. It dissolves in water.
Properties of Mercuric chloride - HgCl2
HgCl2 Mercuric chloride Molecular weight of HgCl2 271.52 g/mol Density of Mercuric chloride 5.43 g/cm3 Boiling point of Mercuric chloride 304 °C Melting point of Mercuric chloride 276 °CMercuric chloride structure - HgCl2
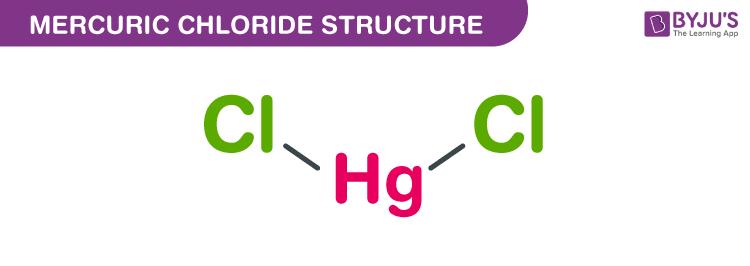
The monoisotopic mass and the exact mass of Mercury (II) chloride is 271.908 g/mol. The number of hydrogen bond donors and the number of hydrogen bond acceptors equal to zero. This compound is canonicalized and has one covalently bonded unit only.
HgCl2 Uses (Mercuric chloride)
- Mercuric chloride is used in the preservation of anatomical specimens.
- Used in leather tanning.
- Used in the manufacturing of ink for mercurography.
- Used as a reagent in analytical chemistry.
- Used in disinfectant, antiseptic.
- Used in photography as an intensifier.
- Used as a catalyst in the conversion of acetylene to vinyl chloride.
- Its solution is as a dip for bulb and tubers.
- Used in dry battery cases.
- Used as an ant repellent.
Production of Mercuric chloride
Mercury (II) chloride is obtained by treating chlorine with mercury (I) chloride or mercury by the and adding hydrochloric acid (HCl) to a hot, concentrated solution of nitrate:
HgNO3 + 2 HCl → HgCl2 + H2O + NO2
Heating a mixture of HgSO4 and sodium chloride (NaCl) gives volatile Mercury (II) chloride, which forms small rhombic crystals. As the temperature increases its solubility increases.
Health hazards:
Mercury dichloride is considered an extremely toxic compound. Any form of mercury is poisonous when absorbed. Probable lethal dosage is 5-50 mg/kg. It is toxic salt of mercury. It attacks the renal systems and gastrointestinal tract.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the uses of mercuric chloride?
Mercuric chloride is primarily used as a catalyst for the conversion of acetylene to vinyl chloride, which is the precursor of polyvinyl chloride. Occasionally, mercuric chloride is used to form an amalgam of metals like aluminium. Chemicals and analytical samples can use mercuric chloride as a stabilizing agent.
How can mercuric chloride be prepared?
Mercuric chloride is generally obtained via the action of chlorine on mercury or mercury(I) chloride. It can also be created by adding hydrochloric acid to a dry concentrated mercury(I) compound solution such as nitrate. Mercuric chloride can also be obtained by the chlorine action on mercury or mercury(I) chloride.
Is mercuric chloride toxic?
Mercuric chloride is highly toxic both directly and as a cumulative toxin. This toxicity is due not only due to the content of mercury but also due to the corrosive properties of this compound, which can cause significant internal damage, including stomach, mouth and throat ulcers, and corrosive bowel damage.
Learn more about the Structure, physical and chemical properties of HgCl2 from the experts at BYJU’S.
Link nội dung: https://sgk.edu.vn/hgcl-a69662.html